
One should also look for any malocclusion, trismus, or facial asymmetry. A careful intraoral examination should be performed sublingual hematoma is suggestive of an occult mandibular fracture. On physical examination, one should inspect the maxillofacial area for deformity, including ecchymosis and edema.
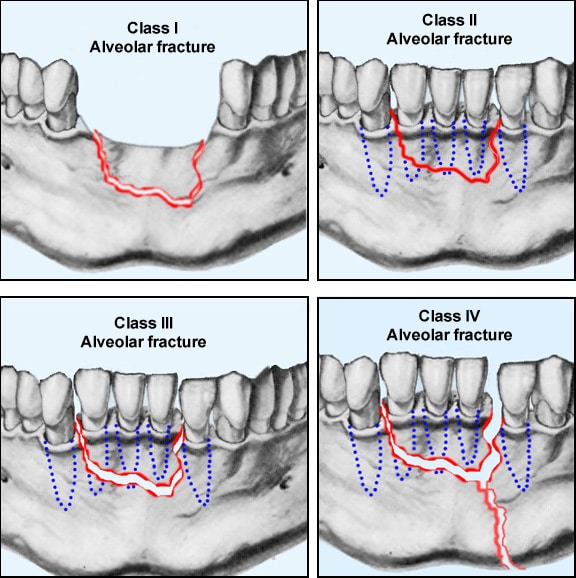
Mandibular fracture from an altercation is more likely to be single, simple, and nondisplaced. In a motor vehicle accident, the patient usually suffers from multiple, compound, or communicated mandibular fractures. Determining the mechanism of injury is important. Malocclusion, a decreased range of movement of the temporomandibular joint, trismus, or lower lip numbness can also be present. Patients will present with mandibular pain, facial asymmetry, deformity, and dysphagia. Follow up with the oral and maxillofacial surgeon or pediatric dentist is indicated. In the pediatric population, any fracture of the mandible may damage permanent teeth. Patients with a mandibular fracture that have wisdom teeth also have a higher infection risk (16.6%) when compared with the ones without wisdom teeth (9.5%). The presence of lower wisdom teeth may increase the risk of fracture of the angle of the mandible. The most common associated injuries include head injuries (39%), head and neck laceration (30%), midface fractures (28%), ocular injuries (16%), nasal fractures (12%), and cervical spine fractures (11%) Patients with mandibular fractures frequently have other associated injuries (43%). Loose teeth and intraoral lacerations with or without bony step-offs may be present as well. Damage to the inferior alveolar nerve may result in anesthesia to the lower lip and chin. ĭepending on the fracture locations, the patient can present with trismus, dental malocclusion, swelling, and tenderness externally and intraorally. Mandibular fractures are favorable when muscles tend to draw the fracture fragments together and unfavorable when muscle forces displace fracture fragments. An example of a favorable fracture is an obliquely-oriented fracture just anterior to the angle, with the superior aspect of the fracture line situated posterior to the inferior aspect this configuration causes the masseter to pull the fragments together and stabilize the fracture, meaning that surgical reduction may not be required. Mandible fractures can be classified by favorableness, based on the association between the direction of the fracture line and the way muscle action either reduces or distracts the fracture fragments. In assault cases, the angle is the most common fractured site. In automobile accidents, the condyle was the most common fracture site whereas, the symphysis was most commonly fractured in motorcycle accidents.
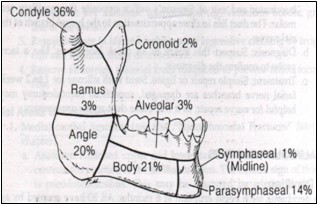
The symphyseal/parasymphyseal area is less commonly fractured, and the ramus and coronoid process are rarely involved. While studies vary in reported fracture frequencies, the most common individual fracture sites are the body, the condyle, and the angle. The most common combination of injuries is a parasymphyseal fracture with a contralateral angle or subcondylar fracture. Because of its ring-like structure, multiple fractures are seen in more than 50% of cases.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
